What Is The Average Age Of Death For Leukemia Patients?
Figuring out the average age of death for people with leukemia is a very important question for many, many reasons. It gives us a way to understand the general picture of this particular kind of cancer. This question really touches on the lives of countless families and individuals. When we talk about "average," we're looking for a single number that helps represent a bigger group of values, so to speak. It helps us get a sense of the typical situation, which can be quite helpful for families and healthcare providers alike.
So, when someone asks, "What is the average age of death for leukemia patients?", they're usually looking for a number that summarizes a lot of different experiences. This number is often what we call the arithmetic mean. You get this by adding up all the ages at which people passed away from leukemia and then dividing that total by the number of people in the group. It's a way to find a middle point, more or less, that can tell us a bit about patterns.
It's important to remember that this "average" is just one piece of the puzzle, you know. Leukemia, actually, is not just one disease; it's a whole group of cancers that affect your blood cells and bone marrow. There are many different types, and each type can behave quite differently. A person's chances of surviving leukemia, and therefore their age at death, really depend on a lot of things. This includes their age when they are diagnosed, their overall health, and even the specific kind of leukemia they have. It's a very complex picture, in a way.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Averages in Health Data
- Leukemia: A Look at the Blood Cancer
- Age as a Major Factor in Leukemia Outcomes
- Different Types of Leukemia and Their Outlook
- Other Factors That Influence Life Expectancy
- Leukemia Statistics: New Cases and Deaths
- Younger Patients and Long-Term Survival
- Treatment Advances and Their Impact
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Finding Support and More Information
Understanding Averages in Health Data
When we talk about an average, especially in something as serious as health, it's pretty much a way to simplify a lot of numbers into one representative value. The most common type, as a matter of fact, is the arithmetic mean. This is just where you add up all the individual numbers and then divide by how many numbers you have. For instance, if you had the ages of several people who passed away from leukemia, you'd sum them up and then divide by the count of those people. This gives you a single number that sort of represents the middle point between all those ages.
An average, you know, can also be a median. If you line up all the ages from the smallest to the largest, the median is the age right in the very middle. This can be helpful because it's not as affected by extremely high or low values, which is sometimes the case with the mean. Whether we're calculating student test scores or trying to figure out the average income in a town, understanding what an average means is truly important for making sense of numerical information. It helps us get a general idea, or a typical level, of a group.
Sometimes, too, you might hear about a "weighted arithmetic mean." This is a bit different from a regular average because some of the numbers in the data set contribute more to the final average than others. It's like some pieces of information have more "weight" than others. In the context of health, this could mean certain factors are given more importance when calculating an average outcome, although that's not typically how the "average age of death" is calculated for general statistics. But it's good to know there are different ways to think about averages, you know.
- Sophie Rain Spiderman Video T
- Mr Hands
- Kalogeras Sisters House Location Google Maps
- J Howard Marshall
- Jeanie Galbraith Age
Leukemia: A Look at the Blood Cancer
Leukemia is a type of cancer that primarily affects your white blood cells. It's a condition that starts in your bone marrow, which is the soft, spongy tissue inside your bones where blood cells are made. Basically, what happens is that blood stem cells in the bone marrow start to develop genetic changes. These changes cause white blood cells, which are also called leukocytes, to grow abnormally. They grow too quickly, and they don't die off when they should, which is a big problem. This leads to a rapid production of these abnormal white blood cells, crowding out healthy cells.
While many people, actually, might think of leukemia as something that mainly affects children, it's important to understand that it can develop at any age. It's not just a childhood cancer. In fact, some types of leukemia are more common in adults, and the risk for certain kinds tends to increase with age. This is why the question of the average age of death for leukemia patients is so relevant, because it varies quite a bit depending on the specific circumstances of the person and their disease. It's a very serious condition, to be sure.
How Leukemia Starts
The beginning of leukemia, in a way, is rooted in the bone marrow. This is where your body's blood stem cells reside. These cells are like the raw materials for all your different blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. With leukemia, these stem cells undergo certain genetic changes, or mutations, that cause them to behave in a very unusual manner. Instead of maturing into healthy, working white blood cells, they become abnormal. These abnormal cells multiply rapidly and don't function as they should. They also, quite literally, avoid being destroyed by the body's immune system, which is their job.
This overproduction of faulty white blood cells can then lead to a range of problems. These abnormal cells can build up in the bone marrow, making it hard for the marrow to produce enough healthy blood cells. They can also spill out into the bloodstream and spread to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, and even the central nervous system. So, it's a condition that affects your blood and bone marrow, and it can impact various systems in your body, you know.
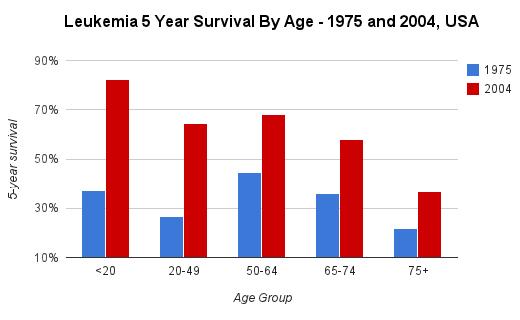
Age as a Major Factor in Leukemia Outcomes
When we talk about how long someone might live with leukemia, or what their age at death might be, age itself is a very, very significant factor. It's one of the most important things that influences a person's chances of surviving this type of cancer. For example, some types of leukemia are more aggressive in older adults, or their bodies might not handle the intense treatments as well as younger people can. This means that the "average age of death" can be quite different depending on the specific type of leukemia and the age group being looked at.
For instance, one common type, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), typically affects adults over the age of 45. The average age at diagnosis for AML, in fact, is around 69 years old. This suggests that older adults are more commonly diagnosed with this particular form. While AML can be serious, especially for patients over 60, it's actually treatable and potentially curable for younger people and those who have certain disease subtypes. This highlights how age plays a huge role, not just in diagnosis, but also in the effectiveness of treatment and the overall outlook. It's a pretty clear pattern, you see.
Similarly, death rates from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are higher among older adults, particularly those who are 75 and older. This again shows how increasing age can be linked to a less favorable prognosis. Younger patients, like those 55 years old or less, with CLL, are a group whose outcomes are still being better understood, especially with modern treatments and ways of looking at their disease. So, age is a really important piece of information when considering leukemia and its impact on life expectancy, in some respects.
Different Types of Leukemia and Their Outlook
Leukemia isn't just one illness; it's a collection of different cancers, and each kind has its own set of characteristics and typical outcomes. Understanding these differences is pretty important when we consider the average age of death for leukemia patients, because the averages can vary quite a bit from one type to another. Some types of leukemia, for instance, tend to progress very quickly, while others move along much more slowly. This distinction, in a way, greatly affects how the disease is treated and what a person's life expectancy might be.
The type of leukemia someone has is, actually, one of the biggest determinants of their prognosis. For example, the outlook for people with chronic myeloid leukemia is often quite good, especially compared to some other forms. On the other hand, acute myeloid leukemia can be very aggressive and requires immediate, intensive treatment. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, generally, tends to have a better outlook than most other types of leukemia, which is good news for many patients. These differences mean that a single "average age of death" for all leukemia types combined might not tell the whole story, you know.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
Chronic myeloid leukemia, also known as chronic myelogenous leukemia, often comes with a rather good prognosis these days. Both the survival rates and the life expectancy for people living with CML have improved considerably. This dramatic improvement, in fact, happened after a specific type of medication was introduced. This medication, called imatinib mesylate, was the very first tyrosine kinase inhibitor, or TKI. It really changed how CML was treated. Before TKIs, the outlook for CML was much less hopeful, but now, it's a different story. The average age of death for CML patients has likely shifted upwards due to these effective treatments, which is a very positive development.
The rate of new cases of chronic myeloid leukemia, you know, has been observed at about 2.0 per 100,000 men and women per year. The death rate for CML is quite low in comparison, at about 0.3 per 100,000 men and women per year. These numbers, actually, reflect the significant progress made in managing this particular type of leukemia. It's a clear example of how advancements in medicine can truly change the course of a disease and extend lives, sometimes quite dramatically. This really highlights the impact of targeted therapies, in a way.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of leukemia where the average age at diagnosis is around 69. It typically affects adults who are over the age of 45. The American Cancer Society states that about one in three leukemia diagnoses in adults involves AML. While it can be a very serious condition, especially for those over age 60, AML is treatable and can even be potentially curable for younger individuals and those with certain specific subtypes of the disease. This difference based on age and subtype is pretty important for understanding outcomes, you know.
The statistics for acute myeloid leukemia show a rate of new cases at about 4.3 per 100,000 men and women per year. The death rate for AML is higher than for CML, coming in at 2.7 per 100,000 men and women per year. These figures, actually, reflect the more aggressive nature of AML compared to CML. The treatment for AML is often very intensive, and while it can be effective, the outcomes can vary widely depending on the patient's age, overall health, and the specific genetic characteristics of their AML. It's a really challenging disease, in some respects.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) generally tends to have a better outlook than most other types of leukemia. However, the life expectancy with CLL can vary quite a bit, depending on several important factors. These include the person's age at the time they are diagnosed, any other health conditions they might have, the stage of the disease when it's found, certain genetic changes within the cancer cells, and how well they respond to treatments. It's a rather complex mix of things that influence the path of the disease.
Death rates from chronic lymphocytic leukemia are, actually, higher among older adults, especially those who are 75 and older. This again underscores the role that age plays in the prognosis for leukemia patients. The clinical characteristics and outcomes for younger patients, those 55 years old or less, with CLL are still being better understood, particularly with the introduction of modern prognostic biomarkers and new chemoimmunotherapy treatments. These newer approaches are, in a way, improving the outlook for many, many people with CLL, which is very encouraging.
Other Factors That Influence Life Expectancy
Beyond the specific type of leukemia and a person's age, there are several other important factors that can influence their life expectancy and, by extension, the average age of death for leukemia patients. A person's overall health when they are diagnosed, for instance, plays a really big part. Someone who is generally healthy with no other major medical conditions might be able to tolerate more aggressive treatments better than someone who has other serious health issues. This is a pretty clear consideration for doctors when planning care, you know.
The time of diagnosis is also quite significant. Catching leukemia early can sometimes lead to better outcomes, though for some types, the disease might progress quickly regardless. The stage of the disease at diagnosis is another key element. For some cancers, the stage tells you how far the cancer has spread, and this is true for leukemia as well, in a way. Genetic changes within the leukemia cells themselves can also influence how the disease behaves and how it might respond to different treatments. These genetic markers are becoming more and more important for guiding therapy. It's a very detailed picture, actually.
Finally, the response to treatments is, of course, absolutely crucial. People with leukemia have many treatment options available to them today. These treatments can often control the disease and its symptoms, and sometimes even lead to a cure. The effectiveness of these treatments, and how a person's body reacts to them, will ultimately affect their life expectancy. Modern treatments have improved considerably for many types of leukemia, which is good news for patients. So, it's not just about the disease itself, but also about how it's managed, you see.
Leukemia Statistics: New Cases and Deaths
Looking at the broader statistics can give us a general sense of the impact of leukemia across the population. The overall rate of new cases of leukemia, for instance, has been observed at about 14.4 per 100,000 men and women per year. This number, in a way, represents how many people are being diagnosed with some form of leukemia each year in a given population. It helps us understand the general prevalence of the disease. These statistics are collected to help researchers and healthcare providers understand trends and allocate resources, you know.
The death rate for all types of leukemia combined is about 5.8 per 100,000 men and women per year. This figure, actually, tells us how many people are passing away from leukemia each year relative to the population size. It's a very important measure for public health. These rates, when looked at over time, can show us if things are improving or if there are areas where more attention is needed. For example, if the death rate is going down, it suggests that treatments are getting better or that diagnosis is happening earlier. It's a very telling number, in some respects.
When we break these numbers down by specific types, the picture becomes a bit clearer. For chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), the death rate is quite low, at 0.3 per 100,000 men and women per year. This is a testament to the advancements in CML treatment. However, for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the death rate is higher, at 2.7 per 100,000 men and women per year. These specific rates truly underscore the different challenges and successes associated with each leukemia type. It's not just one number for everyone, you see.
Younger Patients and Long-Term Survival
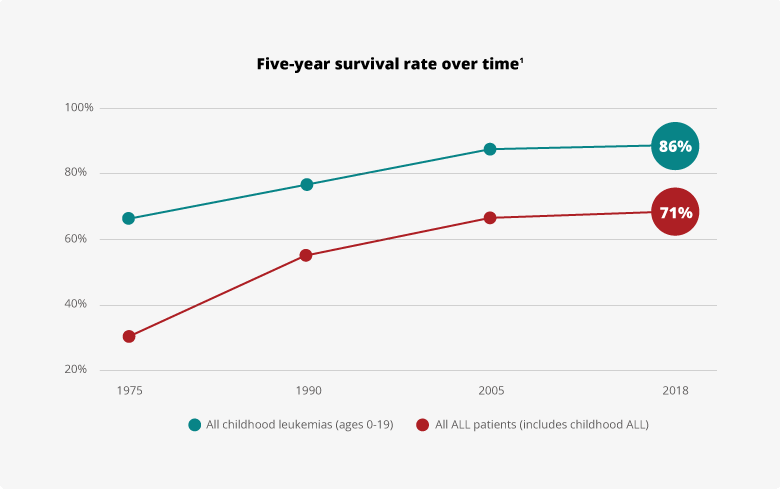
While we often focus on the average age of death, it's also important to consider the experiences of those who survive leukemia, especially younger individuals. Adolescent and young adult leukemia survivors, actually, face a slightly increased risk of mortality compared to the general population for decades after their initial diagnosis. This means that even after they've successfully overcome the initial disease, they might still have ongoing health considerations. Researchers have been looking into these disparities specifically to learn more about the long-term outcomes for patients who have survived their initial diagnosis. It's a very important area of study, you know.
This increased risk for younger survivors could be due to a variety of factors, including the long-term effects of the intensive treatments they received, or perhaps some lingering vulnerabilities related to the disease itself. It highlights that surviving cancer is often just the beginning of a new health journey. Understanding these long-term outcomes helps healthcare providers offer better follow-up care and support for survivors, ensuring they have the best possible quality of life moving forward. It's a pretty complex challenge, in a way.
Treatment Advances and Their Impact
The landscape of leukemia treatment has changed considerably over the years, and these advancements have a direct impact on the average age of death for leukemia patients. As we mentioned, the introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, like imatinib mesylate, truly revolutionized the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. This is just one example of how new medications can dramatically improve survival rates and life expectancy for people living with leukemia. It's a very encouraging area of medical research, you know.
Today, people with leukemia have many treatment options at their disposal. These can include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapies (like TKIs), immunotherapy, and stem cell transplants. The choice of treatment depends on the type of leukemia, its stage, the patient's age, and their overall health. The goal of treatment is often to control the disease and its symptoms, and for many, it can lead to a long period of remission or even a cure. These continuous improvements in treatment mean that the outlook for many leukemia patients is much better than it used to be, which is very positive, in some respects.
The ongoing research into leukemia, including understanding genetic changes and developing more personalized therapies, continues to push the boundaries of what's possible. These efforts are aimed at making treatments more effective and less toxic, ultimately leading to longer and healthier lives for patients. So, while we talk about averages, it's really important to remember that these numbers are always changing as medical science advances. It's a very dynamic field, actually, always striving for better outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions people ask about leukemia and age:
What is the average age of diagnosis for AML?
The average age at diagnosis for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), actually, is around 69 years old. It typically affects adults over the age of 45. This means it's more common in older adults, though it can happen at any age, you know.
Does age affect leukemia survival?
Yes, age very much affects leukemia survival. A person's chances of surviving leukemia depend on a variety of factors, including their age. Some types are more aggressive in older adults, and older bodies might not handle treatments as well. Death rates for chronic lymphocytic leukemia, for instance, are higher among older adults, especially those 75 and older. So, age is a pretty significant factor, in a way.
Are there different types of leukemia with different outcomes?
Absolutely, there are many different types of leukemia, and each one tends to have a different outlook. For example, chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) often comes with a good prognosis, especially with modern treatments. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) tends to have a better outlook than most other types. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) can be more challenging, though it's treatable and potentially curable for younger people. The type of leukemia you have is a very important part of your prognosis, you see.
Finding Support and More Information
Understanding the average age of death for leukemia patients is a starting point, but every person's journey is unique. If you or someone you know is facing a leukemia diagnosis, it's really important to talk with healthcare professionals who can provide personalized information and guidance. They can explain the specific type of leukemia, the available treatment options, and what the outlook might be for that individual. They are the best source for advice, actually.
For more general information about how averages are calculated, you can learn more about average on our site. This can help you understand the statistical tools used to make sense of health data. Also, to explore more about specific types of leukemia and their impact, you might find valuable insights on pages like this page, which can give you a deeper look into survival rates and factors affecting prognosis. Getting good information is a very important step, you know.
Support groups and patient advocacy organizations can also offer valuable resources, emotional support, and practical advice for navigating life with leukemia. Connecting with others who understand what you're going through can be incredibly helpful. It's a very personal journey, and having support makes a big difference. Remember, the information here gives a general picture, but your healthcare team can give you the most accurate details for your specific situation. They are truly your best resource, in some respects.
Leukemia Survival Rate | New Health Advisor

Age - specific Incidence Rates for Acute Myeloid Leukemia in the U.S. (All Races, 2006 - 2010
Leukemia Statistics — Leukemia Research Foundation